CI/CD Pipeline
What is CI-CD?
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment/Delivery (CD) is a method to frequently deliver software to customers by introducing automation into the stages of software development. CI/CD introduces ongoing automation and continuous monitoring throughout the lifecycle of apps, from integration and testing phases to delivery and deployment. Taken together, these connected practices are often referred to as a “CI/CD pipeline” and are supported by development and operations teams working together.
The goal of CI is to establish a consistent and automated method to build, package, and test software. CD picks up the CI artifacts and automate the delivery of application to a selected infrastructure environment.
How CI/CD has been used with microservices?
The Notification Delivery system runs in 2 environments namely - 1. Development (or dev) Environment 2. Production Environment
At the source code level these environments can be distinguished using Git branches. Every microservice has 3 git branches namely development, production and master.
For every commit corresponding to a major-minor update, bug-fix, improvements, patches is built, tested and deployed using a CI/CD pipeline powered by Travis CI.
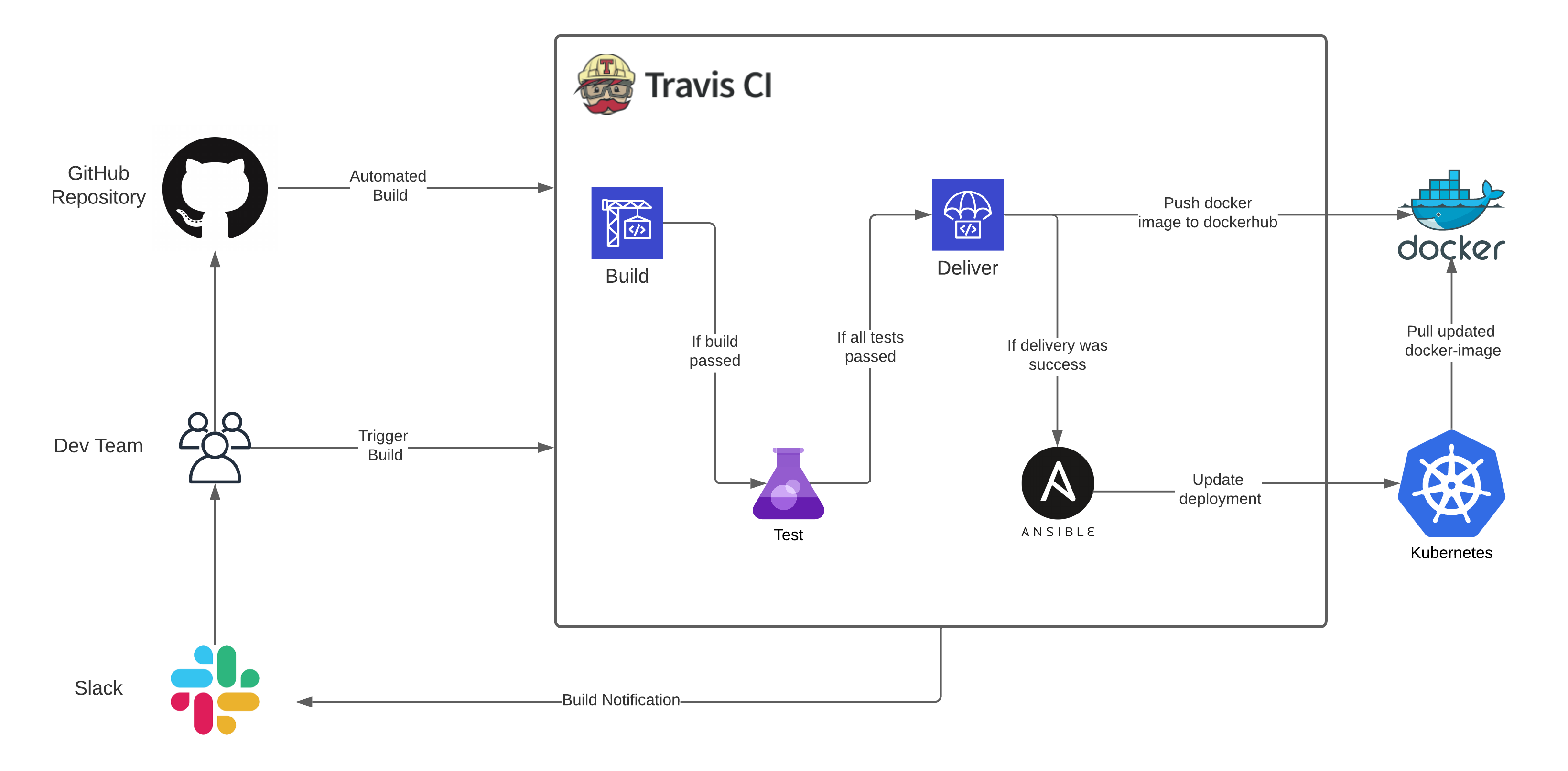

CI/CD stages are different for different branches and environments. Any commit/merge to the development-branch will build the source code and update the development docker-image on DockerHub, same applies for commits/merges on production-branch.
Any update in development environment will be reflected only in the development namespace and any update in production development environment will be reflected only in the production namespace. Updates may include but not limited to the following - 1. Scaling number of pods 2. Updating deployment with newer version of docker image 3. Updaing environment variables and secrets
After the build is complete Ansible updates the Kubernetes deployments by telling it to pull the updated docker-images for the microservices from DockerHub and create/update various resources as defined in the configuration files.